FATF Defense Lawyer
FATF Compliance and Defense Lawyer — a lawyer specializing in compliance with the standards set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and advising on international Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) standards. This legal professional assists clients in effectively adapting to regulatory requirements, minimizing non-compliance risks, and provides legal support during inspections and inquiries from regulatory bodies.
What is FATF?
FATF is the leading global body setting standards in the fields of AML/CFT. Established in 1989 by major global economies, the FATF develops guidelines aimed at safeguarding the integrity of the international financial system through its AML/CFT framework. FATF cannot be regarded as an international organization, as it is neither founded on an international treaty nor governed by a formal charter. FATF has issued the document known as the 40 Recommendations, which are mandatory standards applicable in over 200 jurisdictions worldwide. These standards form a solid legal and regulatory foundation designed to prevent money laundering and terrorism financing. Compliance with these standards is crucial not only for preserving reputation but also for maintaining competitiveness and ensuring access to global capital markets. FATF clearly distinguishes between jurisdictions that uphold high standards and those entrenched in financial instability or strategic regulatory deficiencies. Compliance with FATF Recommendations is fundamental to protecting the international financial system.
What is the FATF Blacklist?
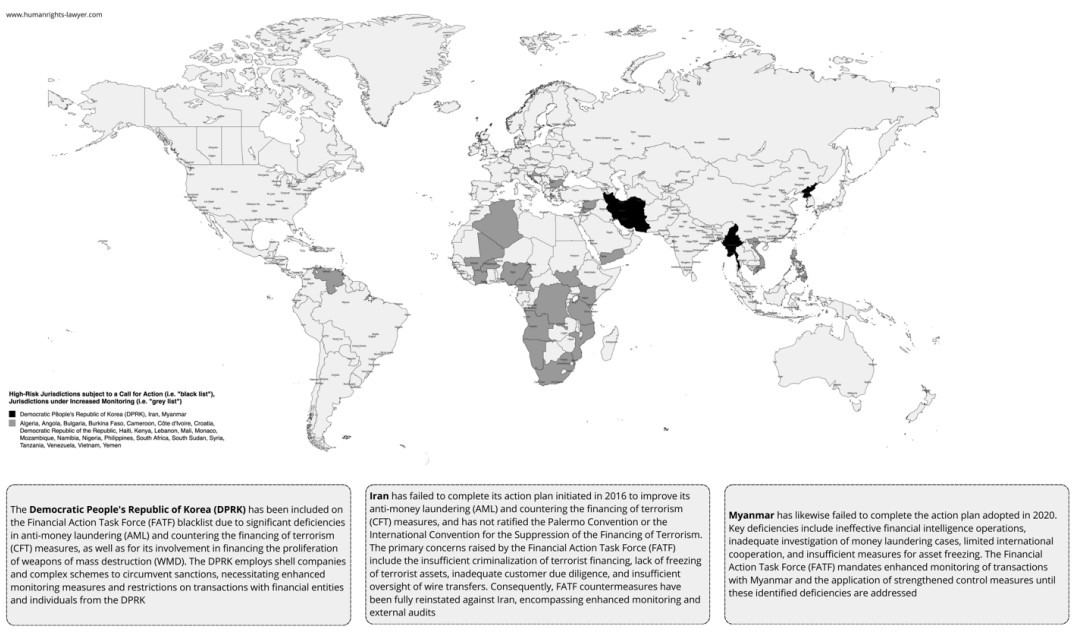
Being placed on the FATF Blacklist (High-Risk Jurisdictions subject to a Call for Action) is akin to receiving an international “badge of dishonor,” signifying a jurisdiction’s inability to adequately implement AML and CFT measures. For financial institutions within such a jurisdiction, this has catastrophic consequences, including severe economic, legal, and reputational repercussions. Access to international financial systems becomes nearly impossible—correspondent banking relationships are severed, funding channels dry up, and any possibility of interacting with foreign counterparts is effectively nullified. Such a status means not only heightened regulatory scrutiny but also fundamental restrictions on the financial sector’s viability. The economic impact of being on the Blacklist ripples through the entire jurisdiction, from reduced foreign investment to destabilized macroeconomic indicators. The global community sends a clear message: “This jurisdiction is not trustworthy, and doing business with it is ill-advised.”
The criteria for inclusion on the FATF blacklist are rigorous and rooted in specific weaknesses in AML and CFT measures:
(а)Low-Level AML/CFT Legislation – urisdictions where legislative and regulatory frameworks fail to ensure effective anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing protections are deemed high-risk. This reflects the inability to address financial crime risks adequately and meet global standards.
(b) Lack of Effective Oversight – countries with insufficient or weak regulatory oversight mechanisms, which result in non-compliance with legislative requirements and an elevated risk of violations, are subject to FATF’s scrutiny. The absence of enforcement power poses a significant threat to international financial integrity.
(c) Non-Cooperation in International Efforts – countries that refuse to cooperate with FATF and other international bodies, neglecting to implement remedial measures to address deficiencies in AML/CFT systems, signal a lack of commitment to global security standards.
(d) Failure to Implement FATF’s 40 Recommendations jurisdictions that do not adopt or enforce FATF’s 40 Recommendations, which constitute the global standard for financial crime prevention, face a heightened risk of being blacklisted. These recommendations cover a range of measures critical for AML and CFT compliance
As of the FATF Blacklist (25 October 2024), three countries are designated: North Korea (DPRK), Iran, and Myanmar.
What is the FATF Greylist?
The FATF Greylist, while not as severe as the Blacklist, still poses a significant challenge. Inclusion on the Greylistindicates substantial deficiencies in AML/CFT measures but also signals the jurisdiction’s willingness to remedy the situation and cooperate with FATF. However, such a status imposes additional obligations, including stringent reporting and systemic reforms. Being on the Greylist complicates financial operations, increases both regulatory and operational costs, undermines trust among international partners, and results in credit rating downgrades. The reputational damage and economic constraints are significant, and exiting the Greylist requires deep, structural transformation of the financial control system and fulfillment of international commitments. 3 Superficial improvements are insufficient—real, substantive reforms that address all aspects of financial regulation and supervision are required.
- 1Lack of up-to-date and adequate AML/CTF laws and regulations
- 2Insufficient control frameworks
- 3Ineffective Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs)
- 4Weak Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measures
- 5Lack of transparency in beneficial ownership information
- 6Low levels of international cooperation
- 7Weak supervision of non-bank institutions
FATF Greylist (25 October 2024) 24 countries are listed, namely Algeria, Angola, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, Croatia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Haiti, Kenya, Lebanon, Mali, Monaco, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Philippines, South Africa, South Sudan, Syria, Tanzania, Venezuela, Vietnam, Yemen.
Implications of Being on FATF List
Inclusion on either the FATF Blacklist or the FATF Greylist represents a profound challenge, capable of destabilizing not only individual financial institutions but also the national economy as a whole. Countries placed on the FATF Blacklist face virtual isolation: access to capital is blocked, international markets are closed, and external trade encounters severe impediments. Failure to meet FATF requirements results in a spiraling increase in compliance costs and severe business disruptions. Economic activity in such countries is paralyzed, leading to further deepening of the crisis. FATF Greylisted jurisdictions also face significant hurdles, yet they retain the potential for rehabilitation, provided they fully comply with all recommendations. Under intense scrutiny from the international community, every step is monitored, leading to intensified regulatory measures, increased operational costs, and diminished trust from international financial partners.
What is FATF’s 40 Recommendations?
The 40 Recommendations of FATF serve as the cornerstone of the global financial regulatory system. They set mandatory standards for all jurisdictions, requiring the implementation of AML/CFT measures, customer due diligence (CDD), transparency regarding beneficial ownership information, and proactive cooperation in international information exchange. Non-compliance with these standards leads to automatic isolation from global financial flows and inflicts considerable damage on economic security. These standards must be integrated into national legal frameworks to ensure resilience against threats and to guarantee that a jurisdiction’s financial system is not exploited for criminal purposes.
The Legal Structure of FATF’s 40 Recommendations
The Recommendations cover key legal areas: the development and coordination of national AML/CFT policies, the criminalization of money laundering and terrorist financing, preventive measures for the financial sector, and ensuring transparency of beneficial ownership for legal persons and arrangements. The structure also includes supervisory and regulatory obligations for competent authorities, enforcement mechanisms, and provisions to facilitate international cooperation. Each Recommendation specifies obligations such as the implementation of Customer Due Diligence (CDD), record-keeping, Suspicious Transaction Reporting (STR), and access to beneficial ownership information for competent authorities. FATF requires member states to adapt these standards flexibly to their legal systems, guided by a risk-based approach (RBA) that focuses resources on identified high-risk areas. The structure and interpretive notes of the Recommendations serve as a basis for assessing countries’ compliance through mutual evaluations and supporting international law enforcement efforts.
How Our FATF Lawyers Can Assist You?
Compliance with international standards is fundamental for preserving the reputation and resilience of any financial institution operating in a global economy. Our lawyers are not merely specialists; they are experts who deeply understand the complexities of FATF regulatory requirements and know how to turn these from potential threats into strategic advantages. We provide the highest level of advisory and support, helping you not only mitigate risks but also strengthen your market position. AML compliance is mandatory for banks, insurance companies, casinos, gaming establishments, lawyers, accountants, cryptocurrency exchanges, forex brokers, and tax consultants. We craft premium, precisely tailored solutions for each of these sectors that minimize regulatory and operational risks, ensuring sustainable growth and adherence to the highest standards of transparency and corporate responsibility. Below are the solutions we offer to provide unparalleled support and strategic growth for your business:
Expert Legal Advocacy in AML Proceedings with U.S. Regulatory
Our attorneys provide expert legal representation in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) matters before key U.S. enforcement and regulatory authorities such as the Department of Justice (DOJ), FinCEN, SEC, CFTC, FINRA, NFA, FDIC, OCC, Federal Reserve, and IRS.
Legal Advisory on AML/CFT Issue
We offer legal advisory services on Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) matters. Our support covers regulatory analysis and assistance with legal compliance issues under FATF standards, ensuring robust legal protection.
AML Policy Structuring and Evaluation
We offer services for the structuring and evaluation of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies and procedures. This includes auditing existing programs and developing internal control regulations to ensure compliance with FATF standards.
Advanced Risk Assessment and Strategic Risk Management
We conduct detailed financial risk analyses and develop strategies for their management, identifying critical risk areas and implementing measures to mitigate them, which contributes to the creation of a sustainable risk management infrastructure.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for High-Risk Counterparties
We conduct enhanced due diligence for high-risk clients, including an analysis of reputational and legal risks. We focus on transparency and heightened diligence measures to protect the business from potential threats.
Advanced Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and KYC Framework Development
We develop and implement Know Your Customer (KYC) programs and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) procedures aimed at risk minimization. This includes client identification, verification, and monitoring to reduce the likelihood of legal infractions.
Beneficial Ownership Structuring and Disclosure Advisory
We provide consulting on beneficial ownership structuring and disclosure in line with FATF international standards. This includes corporate structure audits, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and developing recommendations to enhance transparency and reduce regulatory risks.
In-Depth AML Compliance Training Programs for Personnel
We provide specialized training programs for employees covering key aspects of international Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing (AML/CFT) standards.
We provide comprehensive consulting support to ensure compliance with international FATF standards. Our services include regulatory analysis and integration of internal control systems to minimize regulatory and operational risks. Our goal is to develop customized solutions that facilitate effective risk management and business resilience.

FATF Lawyers FAQ
FATF’s purpose is to establish international standards aimed at preventing the misuse of the financial system for money laundering, terrorism financing, and other illicit activities. FATF sets forth globally accepted norms and recommendations that jurisdictions must implement to ensure the integrity of their financial systems.
FATF publishes updated lists on its official website, indicating jurisdictions that are subject to increased monitoring (Greylist) or those deemed high-risk (Blacklist). These lists are available publicly and are regularly revised to reflect the current status of jurisdictions with respect to compliance.
Businesses should establish robust AML/CFT compliance programs, conduct thorough customer due diligence, regularly assess risk exposure, and ensure ongoing training for their personnel. Implementing effective internal controlsand maintaining open communication with regulatory authorities are crucial for aligning with FATF recommendations.